| Part of a series on |
| Genetic engineering |
|---|
 |
| Genetically modified organisms |
| History and regulation |
| Process |
| Applications |
| Controversies |
Genetically modified foods (GM foods), also known as genetically engineered foods (GE foods), or bioengineered foods are foods produced from organisms that have had changes introduced into their DNA using various methods of genetic engineering. Genetic engineering techniques allow for the introduction of new traits as well as greater control over traits when compared to previous methods, such as selective breeding and mutation breeding.[1]
The discovery of DNA and the improvement of genetic technology in the 20th century played a crucial role in the development of transgenic technology.[2] In 1988, genetically modified microbial enzymes were first approved for use in food manufacture. Recombinant rennet was used in few countries in the 1990s.[3] Commercial sale of genetically modified foods began in 1994, when Calgene first marketed its unsuccessful Flavr Savr delayed-ripening tomato.[4][5] Most food modifications have primarily focused on cash crops in high demand by farmers such as soybean, maize/corn, canola, and cotton. Genetically modified crops have been engineered for resistance to pathogens and herbicides and for better nutrient profiles. The production of golden rice in 2000 marked a further improvement in the nutritional value of genetically modified food.[6] GM livestock have been developed, although, as of 2015[update], none were on the market.[7] As of 2015, the AquAdvantage salmon was the only animal approved for commercial production, sale and consumption by the FDA.[8][9] It is the first genetically modified animal to be approved for human consumption.
Genes encoded for desired features, for instance an improved nutrient level, pesticide and herbicide resistances, and the possession of therapeutic substances, are often extracted and transferred to the target organisms, providing them with superior survival and production capacity.[10][11][12][13][14][15][16] The improved utilization value usually gave consumers benefit in specific aspects.[10][11][15]
There is a scientific consensus[17][18][19][20][21] that currently available food derived from GM crops poses no greater risk to human health than conventional food,[22][23][24][25][26][27][28] but that each GM food needs to be tested on a case-by-case basis before introduction.[29][30][31] Nonetheless, members of the public are much less likely than scientists to perceive GM foods as safe.[32][33][34][35] The legal and regulatory status of GM foods varies by country, with some nations banning or restricting them, and others permitting them with widely differing degrees of regulation,[36][37][38][39] which varied due to geographical, religious, social, and other factors.[10][40][41][42][43]
Definition
[edit]Genetically modified foods are foods produced from organisms that have had changes introduced into their DNA using the methods of genetic engineering as opposed to traditional cross breeding.[44][45] In the U.S., the Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) favor the use of the term genetic engineering over genetic modification as being more precise; the USDA defines genetic modification to include "genetic engineering or other more traditional methods".[46][47]
According to the World Health Organization, "Foods produced from or using GM organisms are often referred to as GM foods."[44]
What constitutes a genetically modified organism (GMO) is not clear and varies widely between countries, international bodies and other communities, has changed significantly over time, and was subject to numerous exceptions based on "convention", such as exclusion of mutation breeding from the EU definition.[48]
Even greater inconsistency and confusion is associated with various "Non-GMO" or "GMO-free" labelling schemes in food marketing, where even products such as water or salt, that do not contain any organic substances and genetic material (and thus cannot be genetically modified by definition) are being labelled to create an impression of being "more healthy."[49][50]
History
[edit]Human-directed genetic manipulation of food began with the domestication of plants and animals through artificial selection at about 10,500 to 10,100 BC.[51]: 1 The process of selective breeding, in which organisms with desired traits (and thus with the desired genes) are used to breed the next generation and organisms lacking the trait are not bred, is a precursor to the modern concept of genetic modification (GM).[51]: 1 [52]: 1 With the discovery of DNA in the early 1900s and various advancements in genetic techniques through the 1970s[2] it became possible to directly alter the DNA and genes within food.
Genetically modified microbial enzymes were the first application of genetically modified organisms in food production and were approved in 1988 by the US Food and Drug Administration.[3] In the early 1990s, recombinant chymosin was approved for use in several countries.[3][53] Cheese had typically been made using the enzyme complex rennet that had been extracted from cows' stomach lining. Scientists modified bacteria to produce chymosin, which was also able to clot milk, resulting in cheese curds.[54]
The first genetically modified food approved for release was the Flavr Savr tomato in 1994.[4] Developed by Calgene, it was engineered to have a longer shelf life by inserting an antisense gene that delayed ripening.[55] China was the first country to commercialize a transgenic crop in 1993 with the introduction of virus-resistant tobacco.[56] In 1995, Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) Potato was approved for cultivation, making it the first pesticide producing crop to be approved in the US.[57] Other genetically modified crops receiving marketing approval in 1995 were: canola with modified oil composition, Bt maize/corn, cotton resistant to the herbicide bromoxynil, Bt cotton, glyphosate-tolerant soybeans, virus-resistant squash, and another delayed ripening tomato.[4]
With the creation of golden rice in 2000, scientists had genetically modified food to increase its nutrient value for the first time.[6]
By 2010, 29 countries had planted commercialized biotech crops and a further 31 countries had granted regulatory approval for transgenic crops to be imported.[58] The US was the leading country in the production of GM foods in 2011, with twenty-five GM crops having received regulatory approval.[59] In 2015, 92% of corn, 94% of soybeans, and 94% of cotton produced in the US were genetically modified varieties.[60]
The first genetically modified animal to be approved for food use was AquAdvantage salmon in 2015.[61] The salmon were transformed with a growth hormone-regulating gene from a Pacific Chinook salmon and a promoter from an ocean pout enabling it to grow year-round instead of only during spring and summer.[62]
A GM white button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) has been approved in the United States since 2016. See §Mushroom below.
The most widely planted GMOs are designed to tolerate herbicides. The use of herbicides presents a strong selection pressure on treated weeds to gain resistance to the herbicide. Widespread planting of GM crops resistant to glyphosate has led to the use of glyphosate to control weeds and many weed species, such as Palmer amaranth, acquiring resistance to the herbicide.[63][64][65]
In 2021, the first CRISPR-edited food has gone on public sale in Japan. Tomatoes were genetically modified for around five times the normal amount of possibly calming[66] GABA.[67] CRISPR was first applied in tomatoes in 2014.[68] Shortly afterwards, the first CRISPR-gene-edited marine animal/seafood and second set of CRISPR-edited food has gone on public sale in Japan: two fish of which one species grows to twice the size of natural specimens due to disruption of leptin, which controls appetite, and the other grows to 1.2 the natural average size with the same amount of food due to disabled myostatin, which inhibits muscle growth.[69][70][71]
Process
[edit]Creating genetically modified food is a multi-step process. The first step is to identify a useful gene from another organism that you would like to add. The gene can be taken from a cell[72] or artificially synthesised,[73] and then combined with other genetic elements, including a promoter and terminator region and a selectable marker.[74] Then the genetic elements are inserted into the targets genome. DNA is generally inserted into animal cells using microinjection, where it can be injected through the cell's nuclear envelope directly into the nucleus, or through the use of viral vectors.[75] In plants the DNA is often inserted using Agrobacterium-mediated recombination,[76][77] biolistics[78] or electroporation. As only a single cell is transformed with genetic material, the organism must be regenerated from that single cell. In plants this is accomplished through tissue culture.[79][80] In animals it is necessary to ensure that the inserted DNA is present in the embryonic stem cells.[76] Further testing using PCR, Southern hybridization, and DNA sequencing is conducted to confirm that an organism contains the new gene.[81]
Traditionally the new genetic material was inserted randomly within the host genome. Gene targeting techniques, which creates double-stranded breaks and takes advantage on the cells natural homologous recombination repair systems, have been developed to target insertion to exact locations. Genome editing uses artificially engineered nucleases that create breaks at specific points. There are four families of engineered nucleases: meganucleases,[82][83] zinc finger nucleases,[84][85] transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs),[86][87] and the Cas9-guideRNA system (adapted from CRISPR).[88][89] TALEN and CRISPR are the two most commonly used and each has its own advantages.[90] TALENs have greater target specificity, while CRISPR is easier to design and more efficient.[90]
By organism
[edit]Crops
[edit]Genetically modified crops (GM crops) are genetically modified plants that are used in agriculture. The first crops developed were used for animal or human food and provide resistance to certain pests, diseases, environmental conditions, spoilage or chemical treatments (e.g. resistance to a herbicide). The second generation of crops aimed to improve the quality, often by altering the nutrient profile. Third generation genetically modified crops could be used for non-food purposes, including the production of pharmaceutical agents, biofuels, and other industrially useful goods, as well as for bioremediation.[91] GM crops have been produced to improve harvests through reducing insect pressure, increase nutrient value and tolerate different abiotic stresses. As of 2018, the commercialised crops are limited mostly to cash crops like cotton, soybean, maize/corn and canola and the vast majority of the introduced traits provide either herbicide tolerance or insect resistance.[91]
The majority of GM crops have been modified to be resistant to selected herbicides, usually a glyphosate or glufosinate based one. Genetically modified crops engineered to resist herbicides are now more available than conventionally bred resistant varieties.[92] Most currently available genes used to engineer insect resistance come from the Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) bacterium and code for delta endotoxins. A few use the genes that encode for vegetative insecticidal proteins.[93] The only gene commercially used to provide insect protection that does not originate from B. thuringiensis is the Cowpea trypsin inhibitor (CpTI). CpTI was first approved for use cotton in 1999 and is currently undergoing trials in rice.[94][95] Less than one percent of GM crops contained other traits, which include providing virus resistance, delaying senescence and altering the plants composition.[96]
Adoption by farmers has been rapid, between 1996 and 2013, the total surface area of land cultivated with GM crops increased by a factor of 100.[97] Geographically though the spread has been uneven, with strong growth in the Americas and parts of Asia and little in Europe and Africa[91] in 2013 only 10% of world cropland was GM, with the US, Canada, Brazil, and Argentina being 90% of that.[21] Its socioeconomic spread has been more even, with approximately 54% of worldwide GM crops grown in developing countries in 2013.[97] Although doubts have been raised,[98] most studies have found growing GM crops to be beneficial to farmers through decreased pesticide use as well as increased crop yield and farm profit.[99][100][101]
Fruits and vegetables
[edit]Long before humans began using transgenics, sweet potato emerged naturally 8000 years ago by embedding of genes from bacteria, that increased its sugar content. Kyndt et al 2015 finds Agrobacterium tumefaciens DNA from this natural transgenic event still in the crop's genome today.[102][103]: 141 [104][105]

Papaya was genetically modified to resist the ringspot virus (PSRV). "SunUp" is a transgenic red-fleshed Sunset papaya cultivar that is homozygous for the coat protein gene PRSV; "Rainbow" is a yellow-fleshed F1 hybrid developed by crossing 'SunUp' and nontransgenic yellow-fleshed "Kapoho".[106] The GM cultivar was approved in 1998[107] and by 2010 80% of Hawaiian papaya was genetically engineered.[108] The New York Times stated, "without it, the state's papaya industry would have collapsed".[108] In China, a transgenic PRSV-resistant papaya was developed by South China Agricultural University and was first approved for commercial planting in 2006; as of 2012 95% of the papaya grown in Guangdong province and 40% of the papaya grown in Hainan province was genetically modified.[109] In Hong Kong, where there is an exemption on growing and releasing any varieties of GM papaya, more than 80% of grown and imported papayas were transgenic.[110][111]
The New Leaf potato, a GM food developed using Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), was made to provide in-plant protection from the yield-robbing Colorado potato beetle.[112] The New Leaf potato, brought to market by Monsanto in the late 1990s, was developed for the fast food market. It was withdrawn in 2001 after retailers rejected it and food processors ran into export problems. In 2011, BASF requested the European Food Safety Authority's approval for cultivation and marketing of its Fortuna potato as feed and food. The potato was made resistant to late blight by adding resistant genes blb1 and blb2 that originate from the Mexican wild potato Solanum bulbocastanum.[113][114] In February 2013, BASF withdrew its application.[115][116] In 2014, the USDA approved a genetically modified potato developed by J. R. Simplot Company that contained ten genetic modifications that prevent bruising and produce less acrylamide when fried. The modifications eliminate specific proteins from the potatoes, via RNA interference, rather than introducing novel proteins.[117][118]
As of 2005, about 13% of the Zucchini grown in the US was genetically modified to resist three viruses; that variety is also grown in Canada.[119][120]

In 2013, the USDA approved the import of a GM pineapple that is pink in color and that "overexpresses" a gene derived from tangerines and suppress other genes, increasing production of lycopene. The plant's flowering cycle was changed to provide for more uniform growth and quality. The fruit "does not have the ability to propagate and persist in the environment once they have been harvested", according to USDA APHIS. According to Del Monte's submission, the pineapples are commercially grown in a "monoculture" that prevents seed production, as the plant's flowers aren't exposed to compatible pollen sources. Importation into Hawaii is banned for "plant sanitation" reasons.[121] Del Monte launched sales of their pink pineapples in October 2020, marketed under the name "Pinkglow".[122]
In February 2015 Arctic Apples were approved by the USDA,[123] becoming the first genetically modified apple approved for sale in the US.[124] Gene silencing is used to reduce the expression of polyphenol oxidase (PPO), thus preventing the fruit from browning.[125]
Maize/corn
[edit]Maize/corn used for food and ethanol has been genetically modified to tolerate various herbicides and to express a protein from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) that kills certain insects.[126] About 90% of the corn grown in the US was genetically modified in 2010.[127] In the US in 2015, 81% of corn acreage contained the Bt trait and 89% of corn acreage contained the glyphosate-tolerant trait.[60] Corn can be processed into grits, meal and flour as an ingredient in pancakes, muffins, doughnuts, breadings and batters, as well as baby foods, meat products, cereals and some fermented products. Corn-based masa flour and masa dough are used in the production of taco shells, corn chips and tortillas.[128]
Soy
[edit]Soybeans accounted for half of all genetically modified crops planted in 2014.[96] Genetically modified soybean has been modified to tolerate herbicides and produce healthier oils.[129] In 2015, 94% of soybean acreage in the U.S. was genetically modified to be glyphosate-tolerant.[60]
Rice
[edit]
Golden rice is the most well known GM crop that is aimed at increasing nutrient value. It has been engineered with three genes that biosynthesise beta-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A, in the edible parts of rice.[130] It is intended to produce a fortified food to be grown and consumed in areas with a shortage of dietary vitamin A,[131] a deficiency which each year is estimated to kill 670,000 children under the age of 5[132] and cause an additional 500,000 cases of irreversible childhood blindness.[133] The original golden rice produced 1.6μg/g of the carotenoids, with further development increasing this 23 times.[134] In 2018 it gained its first approvals for use as food.[135]
Wheat
[edit]As of December 2017, genetically modified wheat has been evaluated in field trials, but has not been released commercially.[136][137][138]
Mushroom
[edit]In April 2016, a white button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) modified using the CRISPR technique received de facto approval in the United States, after the USDA said it would not have to go through the agency's regulatory process. The agency considers the mushroom exempt because the editing process did not involve the introduction of foreign DNA, rather several base pairs were deleted from a duplicated gene coding for an enzyme that causes browning causing a 30% reduction in the level of that enzyme.[139]
Livestock
[edit]Genetically modified livestock are organisms from the group of cattle, sheep, pigs, goats, birds, horses and fish kept for human consumption, whose genetic material (DNA) has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. In some cases, the aim is to introduce a new trait to the animals which does not occur naturally in the species, i.e. transgenesis.
A 2003 review published on behalf of Food Standards Australia New Zealand examined transgenic experimentation on terrestrial livestock species as well as aquatic species such as fish and shellfish. The review examined the molecular techniques used for experimentation as well as techniques for tracing the transgenes in animals and products as well as issues regarding transgene stability.[140]
Some mammals typically used for food production have been modified to produce non-food products, a practice sometimes called Pharming.
Salmon
[edit]A GM salmon, awaiting regulatory approval[141][142][8] since 1997,[143] was approved for human consumption by the American FDA in November 2015, to be raised in specific land-based hatcheries in Canada and Panama.[144]
Microbes
[edit]Bacteriophages are an economically significant cause of culture failure in cheese production. Various culture microbes - especially Lactococcus lactis and Streptococcus thermophilus - have been studied for genetic analysis and modification to improve phage resistance. This has especially focused on plasmid and recombinant chromosomal modifications.[145][146]
Derivative products
[edit]Lecithin
[edit]Lecithin is a naturally occurring lipid. It can be found in egg yolks and oil-producing plants. It is an emulsifier and thus is used in many foods. Corn, soy and safflower oil are sources of lecithin, though the majority of lecithin commercially available is derived from soy.[147][148][149][page needed] Sufficiently processed lecithin is often undetectable with standard testing practices.[150][failed verification] According to the FDA, no evidence shows or suggests hazard to the public when lecithin is used at common levels. Lecithin added to foods amounts to only 2 to 10 percent of the 1 to 5 g of phosphoglycerides consumed daily on average.[147][148] Nonetheless, consumer concerns about GM food extend to such products.[151][better source needed] This concern led to policy and regulatory changes in Europe in 2000,[citation needed] when Regulation (EC) 50/2000 was passed[152] which required labelling of food containing additives derived from GMOs, including lecithin.[citation needed] Because of the difficulty of detecting the origin of derivatives like lecithin with current testing practices, European regulations require those who wish to sell lecithin in Europe to employ a comprehensive system of Identity preservation (IP).[153][verification needed][154][page needed]
Sugar
[edit]The US imports 10% of its sugar, while the remaining 90% is extracted from sugar beet and sugarcane. After deregulation in 2005, glyphosate-resistant sugar beet was extensively adopted in the United States. 95% of beet acres in the US were planted with glyphosate-resistant seed in 2011.[155] GM sugar beets are approved for cultivation in the US, Canada and Japan; the vast majority are grown in the US. GM beets are approved for import and consumption in Australia, Canada, Colombia, EU, Japan, Korea, Mexico, New Zealand, Philippines, the Russian Federation and Singapore.[156] Pulp from the refining process is used as animal feed. The sugar produced from GM sugar beets contains no DNA or protein – it is just sucrose that is chemically indistinguishable from sugar produced from non-GM sugar beets.[150][157] Independent analyses conducted by internationally recognized laboratories found that sugar from Roundup Ready sugar beets is identical to the sugar from comparably grown conventional (non-Roundup Ready) sugar beets.[158]
Vegetable oil
[edit]Most vegetable oil used in the US is produced from GM crops canola,[159] maize/corn,[160][161] cotton[162] and soybeans.[163] Vegetable oil is sold directly to consumers as cooking oil, shortening and margarine[164] and is used in prepared foods. There is a vanishingly small amount of protein or DNA from the original crop in vegetable oil.[150][165] Vegetable oil is made of triglycerides extracted from plants or seeds and then refined and may be further processed via hydrogenation to turn liquid oils into solids. The refining process removes all, or nearly all non-triglyceride ingredients.[166]
Other uses
[edit]Animal feed
[edit]Livestock and poultry are raised on animal feed, much of which is composed of the leftovers from processing crops, including GM crops. For example, approximately 43% of a canola seed is oil. What remains after oil extraction is a meal that becomes an ingredient in animal feed and contains canola protein.[167] Likewise, the bulk of the soybean crop is grown for oil and meal. The high-protein defatted and toasted soy meal becomes livestock feed and dog food. 98% of the US soybean crop goes for livestock feed.[168][169] In 2011, 49% of the US maize/corn harvest was used for livestock feed (including the percentage of waste from distillers grains).[170] "Despite methods that are becoming more and more sensitive, tests have not yet been able to establish a difference in the meat, milk, or eggs of animals depending on the type of feed they are fed. It is impossible to tell if an animal was fed GM soy just by looking at the resulting meat, dairy, or egg products. The only way to verify the presence of GMOs in animal feed is to analyze the origin of the feed itself."[171]
A 2012 literature review of studies evaluating the effect of GM feed on the health of animals did not find evidence that animals were adversely affected, although small biological differences were occasionally found. The studies included in the review ranged from 90 days to two years, with several of the longer studies considering reproductive and intergenerational effects.[172]
Enzymes produced by genetically modified microorganisms are also integrated into animal feed to enhance availability of nutrients and overall digestion. These enzymes may also provide benefit to the gut microbiome of an animal, as well as hydrolyse antinutritional factors present in the feed.[173]
Proteins
[edit]The foundation of genetic engineering is DNA, which directs the production of proteins. Proteins are also the common source of human allergens.[174] When new proteins are introduced they must be assessed for potential allergenicity.[175]
Rennet is a mixture of enzymes used to coagulate milk into cheese. Originally it was available only from the fourth stomach of calves, and was scarce and expensive, or was available from microbial sources, which often produced unpleasant tastes. Genetic engineering made it possible to extract rennet-producing genes from animal stomachs and insert them into bacteria, fungi or yeasts to make them produce chymosin, the key enzyme.[176][177] The modified microorganism is killed after fermentation. Chymosin is isolated from the fermentation broth, so that the Fermentation-Produced Chymosin (FPC) used by cheese producers has an amino acid sequence that is identical to bovine rennet.[178] The majority of the applied chymosin is retained in the whey. Trace quantities of chymosin may remain in cheese.[178]
FPC was the first artificially produced enzyme to be approved by the US Food and Drug Administration.[3][53] FPC products have been on the market since 1990 and as of 2015 had yet to be surpassed in commercial markets.[179] In 1999, about 60% of US hard cheese was made with FPC.[180] Its global market share approached 80%.[181] By 2008, approximately 80% to 90% of commercially made cheeses in the US and Britain were made using FPC.[178]
In some countries, recombinant (GM) bovine somatotropin (also called rBST, or bovine growth hormone or BGH) is approved for administration to increase milk production. rBST may be present in milk from rBST treated cows, but it is destroyed in the digestive system and even if directly injected into the human bloodstream, has no observable effect on humans.[182][183][184] The FDA, World Health Organization, American Medical Association, American Dietetic Association and the National Institutes of Health have independently stated that dairy products and meat from rBST-treated cows are safe for human consumption.[185] On 30 September 2010, the United States Court of Appeals, Sixth Circuit, analyzing submitted evidence, found a "compositional difference" between milk from rBGH-treated cows and milk from untreated cows.[186][187] The court stated that milk from rBGH-treated cows has: increased levels of the hormone Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1); higher fat content and lower protein content when produced at certain points in the cow's lactation cycle; and more somatic cell counts, which may "make the milk turn sour more quickly".[187]
Benefits
[edit]Genetically modified foods are usually edited to have some desired characteristics, including certain benefits for surviving extreme environments, an enhanced level to nutrition, the access of therapeutic substances, and the resistance genes to pesticide and herbicides. These characteristics could be beneficial to humans and the environment in certain ways.
Prepare for extreme weather
[edit]Plants that have undergone genetic modification are capable of surviving extreme weather.[10] Genetically modified (GM) food crops can be cultivated in locations with unfavorable climatic conditions on occasion.[11] The quality and yield of genetically modified foods are often improved.[10] These foods tend to grow more quickly than conventionally cultivated ones. Furthermore, the application of genetically modified food could be beneficial in resisting drought and poor soil.[11]
Nutritional enhancement
[edit]Increased levels of specific nutrients in food crops can be achieved by genetic engineering. The study of this technique, sometimes known as nutritional improvement, is already well advanced.[10] Foods are well monitored to gain specific qualities that became practical, for example, concentrated nutraceutical levels and health-promoting chemicals, making them a desirable component of a varied diet.[188] Among the notable breakthroughs of genetic modification is Golden Rice, whose genome is altered by the injection of the vitamin A gene from a daffodil plant conditioning provitamin A production.[10][188] This increases the activity of phytoene synthase, which therefore synthesizes a higher amount of beta-carotene, followed by modification and improvement of the level of iron and bioavailability.[13][15] This affects the rice’s color and vitamin content, which is beneficial in places where vitamin A shortage is common.[10] In addition, increased mineral, vitamin A, and protein content has played a critical role in preventing childhood blindness and iron deficiency anemia.[13]
Lipid composition could also be manipulated to produce desirable traits and essential nutrients.[15] Scientific evidence has shown that inadequate consumption of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids is generally associated with the development of chronic diseases and developmental aberrations.[12][14] Alimentary lipids can be modified to gain an increased saturated fatty acid together with a decreased polyunsaturated fatty acid component. Genes coded for the synthesis of unsaturated fatty acids are therefore introduced into plant cells, increasing the synthesis of polyunsaturated omega-3 acids.[15] This omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid is responsible to lower the level of LDL cholesterol and triglyceride level as well as the incidence rate of cardiovascular diseases.[12][14][15]
Production of therapeutic substances
[edit]The genetically modified organisms, including potato, tomato, and spinach are applied in the production of substances that stimulate the immune system to respond to specific pathogens.[15] With the help of recombinant DNA techniques, the genes encoded for viral or bacterial antigens could be genetically transcribed and translated into plant cells.[15][16] Antibodies are often produced in response to the introduction of antigens, in which the pathological microflora obtains the immune response towards specific antigens. The transgenic organisms are usually applied to use as oral vaccines, which allows the active substances to enter the human digestive system, targeting the alimentary tract in which stimulate a mucosal immune response. This technique has been widely used in vaccine production including rice, maize, and soybeans.[15] Additionally, transgenic plants are widely used as bioreactors in the production of pharmaceutical proteins and peptides, including vaccines, hormones, human serum albumin (HSA), etc. The suitability of transgenic plants can helps meet the demand for the rapid growth of therapeutic antibodies.[14] All this has given new impetus to the development of medicine.[14][15][16]
Health and safety
[edit]There is a scientific consensus[17][18][19][20] that currently available food derived from GM crops poses no greater risk to human health than conventional food,[22][23][24][25][26][27][28] but that each GM food needs to be tested on a case-by-case basis before introduction.[29][30][31] Nonetheless, members of the public are much less likely than scientists to perceive GM foods as safe.[32][33][34][35] The legal and regulatory status of GM foods varies by country, with some nations banning or restricting them, and others permitting them with widely differing degrees of regulation.[36][37][38][39]
Opponents claim that long-term health risks have not been adequately assessed and propose various combinations of additional testing, labeling[189] or removal from the market.[190][191][192][193]
There are no certifications for foods that have been verified to both be genetically modified – in particular in a way that is ensured to be well-understood, safe and environmentally friendly – as well as otherwise organic (i.e. produced without the use of chemical pesticides) in the U.S. and possibly the world, giving consumers the binary choice of either genetically modified food or organic food.[194][195][196]
Testing
[edit]The legal and regulatory status of GM foods varies by country, with some nations banning or restricting them, and others permitting them with widely differing degrees of regulation.[36][37][38][39] Countries such as the United States, Canada, Lebanon and Egypt use substantial equivalence to determine if further testing is required, while many countries such as those in the European Union, Brazil and China only authorize GMO cultivation on a case-by-case basis. In the U.S. the FDA determined that GMOs are "generally recognized as safe" (GRAS) and therefore do not require additional testing if the GMO product is substantially equivalent to the non-modified product.[197] If new substances are found, further testing may be required to satisfy concerns over potential toxicity, allergenicity, possible gene transfer to humans or genetic outcrossing to other organisms.[44]
Some studies purporting to show harm have been discredited, in some cases leading to academic condemnation against the researchers such as the Pusztai affair and the Séralini affair.[21]
Regulation
[edit]
Government regulation of GMO development and release varies widely between countries. Marked differences separate GMO regulation in the U.S. and GMO regulation in the European Union.[39] Regulation also varies depending on the intended product's use. For example, a crop not intended for food use is generally not reviewed by authorities responsible for food safety.[198] European and EU regulation has been far more restrictive than anywhere else in the world: In 2013 only 1 cultivar of maize/corn and 1 cultivar of potato were approved, and eight EU member states did not allow even those.[21]
United States regulations
[edit]In the U.S., three government organizations regulate GMOs. The FDA checks the chemical composition of organisms for potential allergens. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) supervises field testing and monitors the distribution of GM seeds. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is responsible for monitoring pesticide usage, including plants modified to contain proteins toxic to insects. Like USDA, EPA also oversees field testing and the distribution of crops that have had contact with pesticides to ensure environmental safety.[199][better source needed] In 2015 the Obama administration announced that it would update the way the government regulated GM crops.[200]
In 1992 FDA published "Statement of Policy: Foods derived from New Plant Varieties". This statement is a clarification of FDA's interpretation of the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act with respect to foods produced from new plant varieties developed using recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid (rDNA) technology. FDA encouraged developers to consult with the FDA regarding any bioengineered foods in development. The FDA says developers routinely do reach out for consultations. In 1996 FDA updated consultation procedures.[201][202]
The StarLink corn recalls occurred in the autumn of 2000, when over 300 food products were found to contain a genetically modified maize/corn that had not been approved for human consumption.[203] It was the first-ever recall of a genetically modified food.
European regulations
[edit]The European Union's control of genetically modified organisms is a particular part of an image of the promise and limitations of debate as a framework for supranational regulation.[42] The issues posed by the EU’s GMO regulation have caused major problems in agriculture, politics, societies, status, and other fields.[41][42] 12 The EU law regulates the development and use of GMOs by allocating responsibilities to different authorities, public and private, accompanied by limited recognition of public information, consultation, and participation rights.[42] The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR) provided certain rights and protection for GM biotechnology in the EU. However, the value of human dignity, liberty, equality, and solidarity, as well as the status of democracy and law, as emphasized in the European Charter of Fundamental Rights, are considered the ethical framework governing the employment of scientific and technological research and development.[41]
Due to the political, religious, and social differences in EU countries, the EU’s position on GM has been divided geographically, including more than 100 “GM-free” regions. Different regional attitudes to GM foods make it nearly impossible to reach a common agreement on GM foods.[42] In recent years, however, the sense of crisis that this has generated for the European Union has intensified.[43] Some member states, including Germany, France, Austria, Italy, and Luxembourg, have even banned the planting of certain GM food in their countries in response to public resistance to GM foods.[42][43] The whole thing is set against a backdrop of consumers holding the attitude that GM foods are harmful to both the environment and human health, revolting against GM foods in an anti-biotech coalition.[40] The current political deadlock over GM foods is also a consequence of the ban and has yet to be resolved by scientific methods and processes.[43] Public opinion tends to politicize the GM issue, which is the main obstacle to an agreement in the EU.[42]
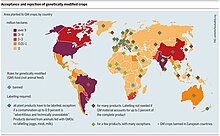
In the United Kingdom, the Food Standards Agency assesses GM foods for their toxicity, nutritional value, and potential to cause allergic reactions. GM foods can be authorised for sale where they present no risk to health, do not mislead consumers, and have nutritional value at least equivalent to non-modified counterparts.[204] The Genetic Technology (Precision Breeding) Act passed into law on 23 March 2023. The UK government said it would allow farmers to "grow crops which are drought and disease resistant, reduce use of fertilisers and pesticides, and help breed animals that are protected from catching harmful diseases".[205]
Labeling
[edit]As of 2015, 64 countries require labeling of GMO products in the marketplace.
US and Canadian national policy is to require a label only given significant composition differences or documented health impacts, although some individual US states (Vermont, Connecticut and Maine) enacted laws requiring them.[206][207][208][209] In July 2016, Public Law 114-214 was enacted to regulate labeling of GMO food on a national basis.
In some jurisdictions, the labeling requirement depends on the relative quantity of GMO in the product. A study that investigated voluntary labeling in South Africa found that 31% of products labeled as GMO-free had a GM content above 1.0%.[210]
In the European Union all food (including processed food) or feed that contains greater than 0.9% GMOs must be labelled.[211]
At the same time, due to lack of single, clear definition of GMO, a number of foods created using genetic engineering techniques (such as mutation breeding) are excluded from labelling and regulation based on "convention" and traditional usage.[48]
The Non-GMO Project is the sole U.S. organization that does verifiable testing and places seals on labels for presence of GMO in products. The "Non-GMO Project Seal" indicates that the product contains 0.9% or less GMO ingredients, which is the European Union's standard for labeling.[212]
Efforts across the world that are being made to help restrict and label GMO's in food involve anti-genetic engineering campaigns and in America the "Just Label It" movement is joining organizations together to call for mandatory labeling.[212]
Detection
[edit]Testing on GMOs in food and feed is routinely done using molecular techniques such as PCR and bioinformatics.[213]
In a January 2010 paper, the extraction and detection of DNA along a complete industrial soybean oil processing chain was described to monitor the presence of Roundup Ready (RR) soybean: "The amplification of soybean lectin gene by end-point polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was successfully achieved in all the steps of extraction and refining processes, until the fully refined soybean oil. The amplification of RR soybean by PCR assays using event-specific primers was also achieved for all the extraction and refining steps, except for the intermediate steps of refining (neutralisation, washing and bleaching) possibly due to sample instability. The real-time PCR assays using specific probes confirmed all the results and proved that it is possible to detect and quantify genetically modified organisms in the fully refined soybean oil. To our knowledge, this has never been reported before and represents an important accomplishment regarding the traceability of genetically modified organisms in refined oils."[214]
According to Thomas Redick, detection and prevention of cross-pollination is possible through the suggestions offered by the Farm Service Agency (FSA) and Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS). Suggestions include educating farmers on the importance of coexistence, providing farmers with tools and incentives to promote coexistence, conducting research to understand and monitor gene flow, providing assurance of quality and diversity in crops, and providing compensation for actual economic losses for farmers.[215]
Regulation methodology design
[edit]This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2022) |
Controversies
[edit]The genetically modified foods controversy consists of a set of disputes over the use of food made from genetically modified crops. The disputes involve consumers, farmers, biotechnology companies, governmental regulators, non-governmental organizations, environmental and political activists and scientists. The major disagreements include whether GM foods can be safely consumed, harm the human body and the environment and/or are adequately tested and regulated.[191][217] The objectivity of scientific research and publications has been challenged.[190] Farming-related disputes include the use and impact of pesticides, seed production and use, side effects on non-GMO crops/farms,[218] and potential control of the GM food supply by seed companies.[190]
The conflicts have continued since GM foods were invented. They have occupied the media, the courts,[219] local, regional, national governments, and international organizations.[citation needed]
"GMO-free" labelling schemes are causing controversies in farming community due to lack of clear definition, inconsistency of their application and are described as "deceptive".[220][221]
Allergenicity
[edit]New allergies could be introduced inadvertently, according to scientists, community groups, and members of the public concerned about the genetic variation of foods.[10] An example involves the methionine rich soybean production.[15] Methionine is an amino acid obtained by synthesizing substances derived from Brazil nuts, which could be an allergen.[15][222] A gene from the Brazil nut was inserted into soybeans during laboratory trials.[11][222] Because it was discovered that those who were allergic to Brazil nuts could also be allergic to genetically modified soybeans, the experiment was stopped.[10][223] In vitro assays such as RAST or serum from people allergic to the original crop could be applied to test the allergenicity of GM goods with known source of the gene.[10] This was established in GM soybeans that expressed Brazil nut 2S proteins and GM potatoes that expressed cod protein genes.[11] The expression and synthesis of new proteins that were previously unavailable in parental cells were achieved by gene transfer from the cells of one organism to the nuclei of another organism. The potential risks of allergy that may develop with the intake of transgenic food come from the amino acid sequence in protein formation.[188] However, there have been no reports of allergic reactions to currently approved GM foods for human consumption, and experiments showed no measurable difference in allergenicity between GM and non-GM soybeans.[10][188][224][225]
Resistance genes
[edit]Scientists suggest that consumers should also pay attention to the health issues associated with the utilizations of pesticide-resistant and herbicide-resistant plants.[11] The ‘Bt’ genes cause insect resistance in today's GM crops; however, other methods to confer insect resistance are in the works.[226] The Bt genes are usually obtained from the soil bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis, and they can generate a protein that breaks down in the insect’s gut, releasing a toxin called delta-endotoxin, which causes paralysis and death.[43] Concerns about resistance and off-target effects of crops expressing Bt toxins, consequences of transgenic herbicide-tolerant plants caused by the use of herbicide, and the transfer of gene expression from GM crops via vertical and horizontal gene transfer are all related to the expression of transgenic material.[41]
Environmental Impacts
[edit]Another concern raised by ecologists is the possible spread of the pest-resistant genes to wildlife.[10][43] This is an example of gene pollution, which is often associated with a decrease in biodiversity, proliferation resistant weeds, and the formation of new pests and pathogens.[227][226]
Studies have proven that herbicide resistant pollen from transgenic rapeseed could spread up to 3 km, while the average gene spread of transgenic crops is 2 km and even reach to maximum 21 kilometers.[227] The high aggressiveness of these GM crops could cause certain disasters by competing with traditional crops for water, light, and nutrients.[222] Crossbreeding of spreading pollens with the surrounding organisms has led to the introduction of the modified resistant genes.[11] An international database that demonstrated genetic contaminations with undesired seeds has been a major problem due to the expansion of field trials and commercially viable cultivation of GM crops around the world.[227][222] Even a decrease in the number of one pest under the impact of a pest-resistant weed could increase the population of other pests that compete with it.[11] Beneficial insects, so named because they prey on crop pests, were also exposed to dangerous doses of Bt.[10]
Other concerns
[edit]The introduction of GM crops in place of more locally adapted varieties could lead to long-term negative effects on the entire agricultural system.[16] Much of the concern with GM technology involves encoding genes that increase or decrease biochemicals. Alternatively, the newly programmed enzyme might result in the consumption of the substrate, forming and accumulating the products.[10]
In terms of socioeconomics, GM crops are usually dependent on high levels of external products, for example, pesticides and herbicides, which limit GM crops to high-input agriculture. This, coupled with the widespread patents held on GM crops, limited farmers’ trading rights over the harvested seeds without paying royalties. Other arguments against GM crops held by some opponents are based on the high costs of isolating and distributing GM crops over non-GM crops.[16]
Consumers could be categorized based on their attitudes regarding genetically modified foods.[40] The ‘attitudinal’ sector of US consumers could be explained in part by cognitive characteristics that are not always observable. Individual characteristics and values, for example, can play a role in shaping consumer acceptance of biotechnology. The concept of transplanting animal DNA into plants is unsettling for many people.[11] Studies have shown that consumers' attitudes towards GM technology are positively correlated to their knowledge about it.[228] It was found that elevated acceptance of genetic modification is usually associated with a high education level, whereas high levels of perceived risks are associated with the opposite.[40][228] People tend to worry about unpredictable dangers due to the lack of sufficient knowledge to predict or avoid negative impacts.[228]
Another crucial link of the change in consumer attitudes towards genetically modified foods has been shown to be closely related to their interaction with socioeconomic and demographic characteristics, for example, age, ethnicity, residence, and level of consumption.[40][222] Opposition to genetically modified foods could also include religious and cultural groups, because the nature of GM foods goes against what they believe are natural products.[11][222][229] On the one hand, it was found that consumers in most European countries, especially in northern Europe, the UK and Germany, believe that the benefits of GM foods do not outweigh the potential risks. On the other hand, consumers in the United States and other European countries generally hold to view that the risks of GM foods could be far less than the benefits it brought.[188] GM foods are then expected to be supported by more appropriate policies and clearer regulations.[222]
See also
[edit]- List of genetically modified crops
- Genetically modified crops
- Genetically modified food controversies
- Genetically modified organisms
- California Proposition 37 (2012) - rejected labeling initiative
- Pharming (genetics) – use of genetically modified mammals to produce drugs
- Regulation of the release of genetic modified organisms
- StarLink corn recall in 2000
References
[edit]- ^ GM Science Review First Report Archived October 16, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Prepared by the UK GM Science Review panel (July 2003). Chairman Professor Sir David King, Chief Scientific Advisor to the UK Government, P 9
- ^ a b Jackson, DA; Symons, RH; Berg, P (1 October 1972). "Biochemical Method for Inserting New Genetic Information into DNA of Simian Virus 40: Circular SV40 DNA Molecules Containing Lambda Phage Genes and the Galactose Operon of Escherichia coli". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 69 (10): 2904–09. Bibcode:1972PNAS...69.2904J. doi:10.1073/pnas.69.10.2904. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 389671. PMID 4342968.
- ^ a b c d "FDA Approves 1st Genetically Engineered Product for Food". Los Angeles Times. 24 March 1990. Retrieved 1 May 2014.
- ^ a b c James, Clive (1996). "Global Review of the Field Testing and Commercialization of Transgenic Plants: 1986 to 1995" (PDF). The International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications. Retrieved 17 July 2010.
- ^ Weasel, Lisa H. 2009. Food Fray. Amacom Publishing
- ^ a b Ye, Xudong; Al-Babili, Salim; Klöti, Andreas; Zhang, Jing; Lucca, Paola; Beyer, Peter; Potrykus, Ingo (2000-01-14). "Engineering the Provitamin A (β-Carotene) Biosynthetic Pathway into (Carotenoid-Free) Rice Endosperm". Science. 287 (5451): 303–05. Bibcode:2000Sci...287..303Y. doi:10.1126/science.287.5451.303. PMID 10634784. S2CID 40258379.
- ^ "Consumer Q&A". FDA. 2009-03-06. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ^ a b Staff (December 26, 2012). "Draft Environmental Assessment and Preliminary Finding of No Significant Impact Concerning a Genetically Engineered Atlantic Salmon" (PDF). Federal Register. Retrieved January 2, 2013.
- ^ "Press Announcements - FDA takes several actions involving genetically engineered plants and animals for food". www.fda.gov. Office of the Commissioner of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 2015-12-03.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Bawa, A. S.; Anilakumar, K. R. (2012-12-19). "Genetically modified foods: safety, risks and public concerns—a review". Journal of Food Science and Technology. 50 (6): 1035–1046. doi:10.1007/s13197-012-0899-1. ISSN 0022-1155. PMC 3791249. PMID 24426015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Healey, Justin. Organic and genetically modified food. ISBN 978-1-925339-11-6. OCLC 946314501.
- ^ a b c Mahgoub, Sala E. O. (2018). Testing and analysis of GMO-containing foods and feed. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-315-17859-2. OCLC 1100467822.
- ^ a b c Dizon, Francis; Costa, Sarah; Rock, Cheryl; Harris, Amanda; Husk, Cierra; Mei, Jenny (2015-12-28). "Genetically Modified (GM) Foods and Ethical Eating". Journal of Food Science. 81 (2): R287–R291. doi:10.1111/1750-3841.13191. ISSN 0022-1147. PMID 26709962.
- ^ a b c d e Huang, Kunlun (2017). Safety Assessment of Genetically Modified Foods. doi:10.1007/978-981-10-3488-6. ISBN 978-981-10-3487-9.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Kramkowska, Marta (2013). Benefits and risks associated with genetically modified food products. OCLC 922412861.
- ^ a b c d e Spreng, S; Viret, J (2005-03-18). "Plasmid maintenance systems suitable for GMO-based bacterial vaccines". Vaccine. 23 (17–18): 2060–2065. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.01.009. ISSN 0264-410X. PMID 15755571.
- ^ a b Nicolia, Alessandro; Manzo, Alberto; Veronesi, Fabio; Rosellini, Daniele (2013). "An overview of the last 10 years of genetically engineered crop safety research" (PDF). Critical Reviews in Biotechnology. 34 (1): 77–88. doi:10.3109/07388551.2013.823595. PMID 24041244. S2CID 9836802.
We have reviewed the scientific literature on GE crop safety for the last 10 years that catches the scientific consensus matured since GE plants became widely cultivated worldwide, and we can conclude that the scientific research conducted so far has not detected any significant hazard directly connected with the use of GM crops.
The literature about Biodiversity and the GE food/feed consumption has sometimes resulted in animated debate regarding the suitability of the experimental designs, the choice of the statistical methods or the public accessibility of data. Such debate, even if positive and part of the natural process of review by the scientific community, has frequently been distorted by the media and often used politically and inappropriately in anti-GE crops campaigns. - ^ a b "State of Food and Agriculture 2003–2004. Agricultural Biotechnology: Meeting the Needs of the Poor. Health and environmental impacts of transgenic crops". Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
Currently available transgenic crops and foods derived from them have been judged safe to eat and the methods used to test their safety have been deemed appropriate. These conclusions represent the consensus of the scientific evidence surveyed by the ICSU (2003) and they are consistent with the views of the World Health Organization (WHO, 2002). These foods have been assessed for increased risks to human health by several national regulatory authorities (inter alia, Argentina, Brazil, Canada, China, the United Kingdom and the United States) using their national food safety procedures (ICSU). To date no verifiable untoward toxic or nutritionally deleterious effects resulting from the consumption of foods derived from genetically modified crops have been discovered anywhere in the world (GM Science Review Panel). Many millions of people have consumed foods derived from GM plants - mainly maize, soybean and oilseed rape - without any observed adverse effects (ICSU).
- ^ a b Ronald, Pamela (May 1, 2011). "Plant Genetics, Sustainable Agriculture and Global Food Security". Genetics. 188 (1): 11–20. doi:10.1534/genetics.111.128553. PMC 3120150. PMID 21546547.
There is broad scientific consensus that genetically engineered crops currently on the market are safe to eat. After 14 years of cultivation and a cumulative total of 2 billion acres planted, no adverse health or environmental effects have resulted from commercialization of genetically engineered crops (Board on Agriculture and Natural Resources, Committee on Environmental Impacts Associated with Commercialization of Transgenic Plants, National Research Council and Division on Earth and Life Studies 2002). Both the U.S. National Research Council and the Joint Research Centre (the European Union's scientific and technical research laboratory and an integral part of the European Commission) have concluded that there is a comprehensive body of knowledge that adequately addresses the food safety issue of genetically engineered crops (Committee on Identifying and Assessing Unintended Effects of Genetically Engineered Foods on Human Health and National Research Council 2004; European Commission Joint Research Centre 2008). These and other recent reports conclude that the processes of genetic engineering and conventional breeding are no different in terms of unintended consequences to human health and the environment (European Commission Directorate-General for Research and Innovation 2010).
- ^ a b
But see also:
Domingo, José L.; Bordonaba, Jordi Giné (2011). "A literature review on the safety assessment of genetically modified plants" (PDF). Environment International. 37 (4): 734–742. Bibcode:2011EnInt..37..734D. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2011.01.003. PMID 21296423.
In spite of this, the number of studies specifically focused on safety assessment of GM plants is still limited. However, it is important to remark that for the first time, a certain equilibrium in the number of research groups suggesting, on the basis of their studies, that a number of varieties of GM products (mainly maize and soybeans) are as safe and nutritious as the respective conventional non-GM plant, and those raising still serious concerns, was observed. Moreover, it is worth mentioning that most of the studies demonstrating that GM foods are as nutritional and safe as those obtained by conventional breeding, have been performed by biotechnology companies or associates, which are also responsible of commercializing these GM plants. Anyhow, this represents a notable advance in comparison with the lack of studies published in recent years in scientific journals by those companies.
Krimsky, Sheldon (2015). "An Illusory Consensus behind GMO Health Assessment". Science, Technology, & Human Values. 40 (6): 883–914. doi:10.1177/0162243915598381. S2CID 40855100.
I began this article with the testimonials from respected scientists that there is literally no scientific controversy over the health effects of GMOs. My investigation into the scientific literature tells another story.
And contrast:
Panchin, Alexander Y.; Tuzhikov, Alexander I. (January 14, 2016). "Published GMO studies find no evidence of harm when corrected for multiple comparisons". Critical Reviews in Biotechnology. 37 (2): 213–217. doi:10.3109/07388551.2015.1130684. ISSN 0738-8551. PMID 26767435. S2CID 11786594.
Here, we show that a number of articles some of which have strongly and negatively influenced the public opinion on GM crops and even provoked political actions, such as GMO embargo, share common flaws in the statistical evaluation of the data. Having accounted for these flaws, we conclude that the data presented in these articles does not provide any substantial evidence of GMO harm.
The presented articles suggesting possible harm of GMOs received high public attention. However, despite their claims, they actually weaken the evidence for the harm and lack of substantial equivalency of studied GMOs. We emphasize that with over 1783 published articles on GMOs over the last 10 years it is expected that some of them should have reported undesired differences between GMOs and conventional crops even if no such differences exist in reality.and
Yang, Y.T.; Chen, B. (2016). "Governing GMOs in the USA: science, law and public health". Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 96 (4): 1851–1855. Bibcode:2016JSFA...96.1851Y. doi:10.1002/jsfa.7523. PMID 26536836.It is therefore not surprising that efforts to require labeling and to ban GMOs have been a growing political issue in the USA (citing Domingo and Bordonaba, 2011). Overall, a broad scientific consensus holds that currently marketed GM food poses no greater risk than conventional food... Major national and international science and medical associations have stated that no adverse human health effects related to GMO food have been reported or substantiated in peer-reviewed literature to date.
Despite various concerns, today, the American Association for the Advancement of Science, the World Health Organization, and many independent international science organizations agree that GMOs are just as safe as other foods. Compared with conventional breeding techniques, genetic engineering is far more precise and, in most cases, less likely to create an unexpected outcome. - ^ a b c d Freedman, David H. (2013-08-20). "are engineered foods evil?". Scientific American. 309 (3). Springer Nature: 80–85. Bibcode:2013SciAm.309c..80F. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0913-80. ISSN 0036-8733. JSTOR 26017991. PMID 24003560. S2CID 32994342.
- ^ a b "Statement by the AAAS Board of Directors On Labeling of Genetically Modified Foods" (PDF). American Association for the Advancement of Science. October 20, 2012. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
The EU, for example, has invested more than €300 million in research on the biosafety of GMOs. Its recent report states: "The main conclusion to be drawn from the efforts of more than 130 research projects, covering a period of more than 25 years of research and involving more than 500 independent research groups, is that biotechnology, and in particular GMOs, are not per se more risky than e.g. conventional plant breeding technologies." The World Health Organization, the American Medical Association, the U.S. National Academy of Sciences, the British Royal Society, and every other respected organization that has examined the evidence has come to the same conclusion: consuming foods containing ingredients derived from GM crops is no riskier than consuming the same foods containing ingredients from crop plants modified by conventional plant improvement techniques.
Pinholster, Ginger (October 25, 2012). "AAAS Board of Directors: Legally Mandating GM Food Labels Could "Mislead and Falsely Alarm Consumers"" (PDF). American Association for the Advancement of Science. Retrieved August 30, 2019. - ^ a b European Commission. Directorate-General for Research (2010). A decade of EU-funded GMO research (2001–2010) (PDF). Directorate-General for Research and Innovation. Biotechnologies, Agriculture, Food. European Commission, European Union. doi:10.2777/97784. ISBN 978-92-79-16344-9. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
- ^ a b "ISAAA Summary of AMA Report on Genetically Modified Crops and Foods". ISAAA. January 2001. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
A report issued by the scientific council of the American Medical Association (AMA) says that no long-term health effects have been detected from the use of transgenic crops and genetically modified foods, and that these foods are substantially equivalent to their conventional counterparts.
- ^ a b "Featured CSA Report: Genetically Modified Crops and Foods (I-00) Full Text". American Medical Association. Archived from the original on 10 June 2001.
Crops and foods produced using recombinant DNA techniques have been available for fewer than 10 years and no long-term effects have been detected to date. These foods are substantially equivalent to their conventional counterparts.
- ^ a b "Report 2 of the Council on Science and Public Health (A-12): Labeling of Bioengineered Foods" (PDF). American Medical Association. 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-09-07. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
"Bioengineered foods have been consumed for close to 20 years, and during that time, no overt consequences on human health have been reported and/or substantiated in the peer-reviewed literature".
- ^ a b "Restrictions on Genetically Modified Organisms: United States. Public and Scholarly Opinion". Library of Congress. June 30, 2015. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
Several scientific organizations in the US have issued studies or statements regarding the safety of GMOs indicating that there is no evidence that GMOs present unique safety risks compared to conventionally bred products. These include the National Research Council, the American Association for the Advancement of Science, and the American Medical Association. Groups in the US opposed to GMOs include some environmental organizations, organic farming organizations, and consumer organizations. A substantial number of legal academics have criticized the US's approach to regulating GMOs.
- ^ a b National Academies Of Sciences, Engineering; Division on Earth Life Studies; Board on Agriculture Natural Resources; Committee on Genetically Engineered Crops: Past Experience Future Prospects (2016). Genetically Engineered Crops: Experiences and Prospects. The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (US). p. 149. doi:10.17226/23395. ISBN 978-0-309-43738-7. PMID 28230933. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
Overall finding on purported adverse effects on human health of foods derived from GE crops: On the basis of detailed examination of comparisons of currently commercialized GE with non-GE foods in compositional analysis, acute and chronic animal toxicity tests, long-term data on health of livestock fed GE foods, and human epidemiological data, the committee found no differences that implicate a higher risk to human health from GE foods than from their non-GE counterparts.
- ^ a b "Frequently asked questions on genetically modified foods". World Health Organization. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
Different GM organisms include different genes inserted in different ways. This means that individual GM foods and their safety should be assessed on a case-by-case basis and that it is not possible to make general statements on the safety of all GM foods.
GM foods currently available on the international market have passed safety assessments and are not likely to present risks for human health. In addition, no effects on human health have been shown as a result of the consumption of such foods by the general population in the countries where they have been approved. Continuous application of safety assessments based on the Codex Alimentarius principles and, where appropriate, adequate post market monitoring, should form the basis for ensuring the safety of GM foods. - ^ a b Haslberger, Alexander G. (2003). "Codex guidelines for GM foods include the analysis of unintended effects". Nature Biotechnology. 21 (7): 739–741. doi:10.1038/nbt0703-739. PMID 12833088. S2CID 2533628.
These principles dictate a case-by-case premarket assessment that includes an evaluation of both direct and unintended effects.
- ^ a b Some medical organizations, including the British Medical Association, advocate further caution based upon the precautionary principle:
"Genetically modified foods and health: a second interim statement" (PDF). British Medical Association. March 2004. Retrieved August 30, 2019.In our view, the potential for GM foods to cause harmful health effects is very small and many of the concerns expressed apply with equal vigour to conventionally derived foods. However, safety concerns cannot, as yet, be dismissed completely on the basis of information currently available.
When seeking to optimise the balance between benefits and risks, it is prudent to err on the side of caution and, above all, learn from accumulating knowledge and experience. Any new technology such as genetic modification must be examined for possible benefits and risks to human health and the environment. As with all novel foods, safety assessments in relation to GM foods must be made on a case-by-case basis.
Members of the GM jury project were briefed on various aspects of genetic modification by a diverse group of acknowledged experts in the relevant subjects. The GM jury reached the conclusion that the sale of GM foods currently available should be halted and the moratorium on commercial growth of GM crops should be continued. These conclusions were based on the precautionary principle and lack of evidence of any benefit. The Jury expressed concern over the impact of GM crops on farming, the environment, food safety and other potential health effects.
The Royal Society review (2002) concluded that the risks to human health associated with the use of specific viral DNA sequences in GM plants are negligible, and while calling for caution in the introduction of potential allergens into food crops, stressed the absence of evidence that commercially available GM foods cause clinical allergic manifestations. The BMA shares the view that there is no robust evidence to prove that GM foods are unsafe but we endorse the call for further research and surveillance to provide convincing evidence of safety and benefit. - ^ a b Funk, Cary; Rainie, Lee (January 29, 2015). "Public and Scientists' Views on Science and Society". Pew Research Center. Archived from the original on January 9, 2019. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
The largest differences between the public and the AAAS scientists are found in beliefs about the safety of eating genetically modified (GM) foods. Nearly nine-in-ten (88%) scientists say it is generally safe to eat GM foods compared with 37% of the general public, a difference of 51 percentage points.
- ^ a b Marris, Claire (2001). "Public views on GMOs: deconstructing the myths". EMBO Reports. 2 (7): 545–548. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kve142. PMC 1083956. PMID 11463731.
- ^ a b Final Report of the PABE research project (December 2001). "Public Perceptions of Agricultural Biotechnologies in Europe". Commission of European Communities. Archived from the original on 2017-05-25. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
- ^ a b Scott, Sydney E.; Inbar, Yoel; Rozin, Paul (2016). "Evidence for Absolute Moral Opposition to Genetically Modified Food in the United States" (PDF). Perspectives on Psychological Science. 11 (3): 315–324. doi:10.1177/1745691615621275. PMID 27217243. S2CID 261060.
- ^ a b c "Restrictions on Genetically Modified Organisms". Library of Congress. June 9, 2015. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
- ^ a b c Bashshur, Ramona (February 2013). "FDA and Regulation of GMOs". American Bar Association. Archived from the original on June 21, 2018. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
- ^ a b c Sifferlin, Alexandra (October 3, 2015). "Over Half of E.U. Countries Are Opting Out of GMOs". Time. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
- ^ a b c d Lynch, Diahanna; Vogel, David (April 5, 2001). "The Regulation of GMOs in Europe and the United States: A Case-Study of Contemporary European Regulatory Politics". Council on Foreign Relations. Archived from the original on September 29, 2016. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e Skogstad, Grace (2011-01-13). "Contested Accountability Claims and GMO Regulation in the European Union". JCMS: Journal of Common Market Studies. 49 (4): 895–915. doi:10.1111/j.1468-5965.2010.02166.x. ISSN 0021-9886. S2CID 154570139.
- ^ a b c d Thayyil, Naveen (2014). Biotechnology regulation and GMOs law, technology and public contestations in Europe. Edward Elgar Pub. Ltd. ISBN 978-1-84844-564-2. OCLC 891882521.
- ^ a b c d e f g Weimer, Maria (2015-05-24). "Risk Regulation and Deliberation in EU Administrative Governance-GMO Regulation and Its Reform". European Law Journal. 21 (5): 622–640. doi:10.1111/eulj.12140. ISSN 1351-5993. S2CID 154666745.
- ^ a b c d e f Wickson, Fern (December 2014). "Environmental protection goals, policy & publics in the European regulation of GMOs". Ecological Economics. 108: 269–273. Bibcode:2014EcoEc.108..269W. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2014.09.025. ISSN 0921-8009.
- ^ a b c World Health Organization. "Frequently asked questions on genetically modified foods". Retrieved 29 March 2016.
- ^ "Genetically engineered foods". University of Maryland Medical Center. Archived from the original on 2016-02-14. Retrieved 14 Feb 2016.
- ^ "Glossary of Agricultural Biotechnology Terms". United States Department of Agriculture. 27 February 2013. Retrieved 29 September 2015.
- ^ "Questions & Answers on Food from Genetically Engineered Plants". US Food and Drug Administration. 22 Jun 2015. Archived from the original on June 23, 2015. Retrieved 29 September 2015.
- ^ a b "Organisms obtained by mutagenesis are GMOs and are, in principle, subject to the obligations laid down by the GMO Directive" (PDF). curia.europa.eu. Retrieved 2019-01-05.
- ^ Knutson, Jonathan (May 28, 2018). "A sad day for our society when salt is labeled non-GMO". Agweek. Retrieved 2021-07-09.
- ^ "Non GMO salt? Water? Food companies exploit GMO free labels, misleading customers, promoting misinformation". Genetic Literacy Project. 2015-08-24. Retrieved 2021-07-09.
- ^ a b Daniel Zohary; Maria Hopf; Ehud Weiss (2012). Domestication of Plants in the Old World: The Origin and Spread of Plants in the Old World. Oxford University Press.
- ^ Clive Root (2007). Domestication. Greenwood Publishing Groups.
- ^ a b Staff, National Centre for Biotechnology Education (2006). "Chymosin". Archived from the original on May 22, 2016.
- ^ Campbell-Platt, Geoffrey (26 August 2011). Food Science and Technology. Ames, Iowa: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-4443-5782-0.
- ^ Bruening, G.; Lyons, J. M. (2000). "The case of the FLAVR SAVR tomato". California Agriculture. 54 (4): 6–7. doi:10.3733/ca.v054n04p6 (inactive 2024-07-29).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of July 2024 (link) - ^ James, Clive (2010). "Global Review of the Field Testing and Commercialization of Transgenic Plants: 1986 to 1995: The First Decade of Crop Biotechnology". ISAAA Briefs No. 1: 31.
- ^ Genetically Altered Potato Ok'd For Crops Lawrence Journal-World - 6 May 1995
- ^ Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2011 ISAAA Brief ISAAA Brief 43-2011. Retrieved 14 October 2012
- ^ James, C (2011). "ISAAA Brief 43, Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2011". ISAAA Briefs. Ithaca, New York: International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications (ISAAA). Retrieved 2012-06-02.
- ^ a b c "Adoption of Genetically Engineered Crops in the U.S." Economic Research Service, USDA. Retrieved 26 August 2015.
- ^ "Aquabounty Cleared to Sell Salmon in the USA for Commercial Purposes". FDA. 2019-06-19.
- ^ Bodnar, Anastasia (October 2010). "Risk Assessment and Mitigation of AquAdvantage Salmon" (PDF). ISB News Report. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-03-08. Retrieved 2016-01-22.
- ^ Culpepper, Stanley A; et al. (2006). "Glyphosate-resistant Palmer amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri) confirmed in Georgia". Weed Science. 54 (4): 620–26. doi:10.1614/ws-06-001r.1. S2CID 56236569.
- ^ Gallant, Andre. "Pigweed in the Cotton: A superweed invades Georgia". Modern Farmer.
- ^ Webster, TM; Grey, TL (2015). "Glyphosate-Resistant Palmer Amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri) Morphology, Growth, and Seed Production in Georgia". Weed Science. 63 (1): 264–72. doi:10.1614/ws-d-14-00051.1. S2CID 86300650.
- ^ Boonstra, Evert; de Kleijn, Roy; Colzato, Lorenza S.; Alkemade, Anneke; Forstmann, Birte U.; Nieuwenhuis, Sander (6 October 2015). "Neurotransmitters as food supplements: the effects of GABA on brain and behavior". Frontiers in Psychology. 6: 1520. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01520. PMC 4594160. PMID 26500584.
- ^ "Tomato In Japan Is First CRISPR-Edited Food In The World To Go On Sale". IFLScience. Retrieved 18 October 2021.
- ^ Wang, Tian; Zhang, Hongyan; Zhu, Hongliang (15 June 2019). "CRISPR technology is revolutionizing the improvement of tomato and other fruit crops". Horticulture Research. 6 (1): 77. Bibcode:2019HorR....6...77W. doi:10.1038/s41438-019-0159-x. ISSN 2052-7276. PMC 6570646. PMID 31240102.
- ^ "Japan embraces CRISPR-edited fish". Nature Biotechnology. 40 (1): 10. 1 January 2022. doi:10.1038/s41587-021-01197-8. PMID 34969964. S2CID 245593283. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
- ^ "Startup hopes genome-edited pufferfish will be a hit in 2022". The Japan Times. 5 January 2022. Archived from the original on 17 January 2022. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
- ^ "Gene-edited sea bream set for sale in Japan". thefishsite.com.
- ^ Nicholl DS (2008-05-29). An Introduction to Genetic Engineering. Cambridge University Press. p. 34. ISBN 9781139471787.
- ^ Liang J, Luo Y, Zhao H (2011). "Synthetic biology: putting synthesis into biology". Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Systems Biology and Medicine. 3 (1): 7–20. doi:10.1002/wsbm.104. PMC 3057768. PMID 21064036.
- ^ Berg P, Mertz JE (January 2010). "Personal reflections on the origins and emergence of recombinant DNA technology". Genetics. 184 (1): 9–17. doi:10.1534/genetics.109.112144. PMC 2815933. PMID 20061565.
- ^ Chen I, Dubnau D (March 2004). "DNA uptake during bacterial transformation". Nature Reviews. Microbiology. 2 (3): 241–9. doi:10.1038/nrmicro844. PMID 15083159. S2CID 205499369.
- ^ a b National Research Council (US) Committee on Identifying and Assessing Unintended Effects of Genetically Engineered Foods on Human Health (2004-01-01). Methods and Mechanisms for Genetic Manipulation of Plants, Animals, and Microorganisms. National Academies Press (US).
- ^ Gelvin SB (March 2003). "Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation: the biology behind the "gene-jockeying" tool". Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews. 67 (1): 16–37, table of contents. doi:10.1128/MMBR.67.1.16-37.2003. PMC 150518. PMID 12626681.
- ^ Head G, Hull RH, Tzotzos GT (2009). Genetically Modified Plants: Assessing Safety and Managing Risk. London: Academic Pr. p. 244. ISBN 978-0-12-374106-6.
- ^ Tuomela M, Stanescu I, Krohn K (October 2005). "Validation overview of bio-analytical methods". Gene Therapy. 12 Suppl 1 (S1): S131-8. doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3302627. PMID 16231045.
- ^ Narayanaswamy S (1994). Plant Cell and Tissue Culture. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. pp. vi. ISBN 9780074602775.
- ^ Setlow JK (2002-10-31). Genetic Engineering: Principles and Methods. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 109. ISBN 9780306472800.
- ^ Grizot S, Smith J, Daboussi F, Prieto J, Redondo P, Merino N, Villate M, Thomas S, Lemaire L, Montoya G, Blanco FJ, Pâques F, Duchateau P (September 2009). "Efficient targeting of a SCID gene by an engineered single-chain homing endonuclease". Nucleic Acids Research. 37 (16): 5405–19. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp548. PMC 2760784. PMID 19584299.
- ^ Gao H, Smith J, Yang M, Jones S, Djukanovic V, Nicholson MG, West A, Bidney D, Falco SC, Jantz D, Lyznik LA (January 2010). "Heritable targeted mutagenesis in maize using a designed endonuclease". The Plant Journal. 61 (1): 176–87. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04041.x. PMID 19811621.
- ^ Townsend JA, Wright DA, Winfrey RJ, Fu F, Maeder ML, Joung JK, Voytas DF (May 2009). "High-frequency modification of plant genes using engineered zinc-finger nucleases". Nature. 459 (7245): 442–5. Bibcode:2009Natur.459..442T. doi:10.1038/nature07845. PMC 2743854. PMID 19404258.
- ^ Shukla VK, Doyon Y, Miller JC, DeKelver RC, Moehle EA, Worden SE, Mitchell JC, Arnold NL, Gopalan S, Meng X, Choi VM, Rock JM, Wu YY, Katibah GE, Zhifang G, McCaskill D, Simpson MA, Blakeslee B, Greenwalt SA, Butler HJ, Hinkley SJ, Zhang L, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Urnov FD (May 2009). "Precise genome modification in the crop species Zea mays using zinc-finger nucleases". Nature. 459 (7245): 437–41. Bibcode:2009Natur.459..437S. doi:10.1038/nature07992. PMID 19404259. S2CID 4323298.
- ^ Christian M, Cermak T, Doyle EL, Schmidt C, Zhang F, Hummel A, Bogdanove AJ, Voytas DF (October 2010). "Targeting DNA double-strand breaks with TAL effector nucleases". Genetics. 186 (2): 757–61. doi:10.1534/genetics.110.120717. PMC 2942870. PMID 20660643.
- ^ Li T, Huang S, Jiang WZ, Wright D, Spalding MH, Weeks DP, Yang B (January 2011). "TAL nucleases (TALNs): hybrid proteins composed of TAL effectors and FokI DNA-cleavage domain". Nucleic Acids Research. 39 (1): 359–72. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq704. PMC 3017587. PMID 20699274.
- ^ Esvelt KM, Wang HH (2013). "Genome-scale engineering for systems and synthetic biology". Molecular Systems Biology. 9: 641. doi:10.1038/msb.2012.66. PMC 3564264. PMID 23340847.
- ^ Tan WS, Carlson DF, Walton MW, Fahrenkrug SC, Hackett PB (2012). "Precision Editing of Large Animal Genomes". Advances in Genetics Volume 80. Vol. 80. pp. 37–97. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-404742-6.00002-8. ISBN 9780124047426. PMC 3683964. PMID 23084873.
- ^ a b Malzahn A, Lowder L, Qi Y (2017-04-24). "Plant genome editing with TALEN and CRISPR". Cell & Bioscience. 7: 21. doi:10.1186/s13578-017-0148-4. PMC 5404292. PMID 28451378.
- ^ a b c Qaim M (2016-04-29). "Introduction". Genetically Modified Crops and Agricultural Development. Springer. pp. 1–10. ISBN 9781137405722.
- ^ Darmency H (August 2013). "Pleiotropic effects of herbicide-resistance genes on crop yield: a review". Pest Management Science. 69 (8): 897–904. doi:10.1002/ps.3522. PMID 23457026.
- ^ Fleischer SJ, Hutchison WD, Naranjo SE (2014). "Sustainable Management of Insect-Resistant Crops". Plant Biotechnology. pp. 115–127. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-06892-3_10. ISBN 978-3-319-06891-6.
- ^ "SGK321". GM Approval Database. ISAAA.org. Retrieved 2017-04-27.
- ^ Qiu J (October 2008). "Is China ready for GM rice?". Nature. 455 (7215): 850–2. doi:10.1038/455850a. PMID 18923484.
- ^ a b "Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2014 - ISAAA Brief 49-2014". ISAAA.org. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ^ a b ISAAA 2013 Annual Report Executive Summary, Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2013 ISAAA Brief 46-2013, Retrieved 6 August 2014
- ^ Hakim, Danny (2016-10-29). "Doubts About the Promised Bounty of Genetically Modified Crops". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2017-05-05.
- ^ Areal FJ, Riesgo L, Rodríguez-Cerezo E (February 2013). "Economic and agronomic impact of commercialized GM crops: a meta-analysis". The Journal of Agricultural Science. 151 (1): 7–33. doi:10.1017/S0021859612000111. ISSN 0021-8596. S2CID 85891950.
- ^ Finger R, El Benni N, Kaphengst T, Evans C, Herbert S, Lehmann B, Morse S, Stupak N (2011-05-10). "A Meta Analysis on Farm-Level Costs and Benefits of GM Crops". Sustainability. 3 (5): 743–62. doi:10.3390/su3050743. hdl:20.500.11850/42242.
- ^ Klümper W, Qaim M (2014-11-03). "A meta-analysis of the impacts of genetically modified crops". PLOS ONE. 9 (11): e111629. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9k1629K. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111629. PMC 4218791. PMID 25365303.
- ^ Doucleff, Michaeleen (2015-05-05). "Natural GMO? Sweet Potato Genetically Modified 8,000 Years Ago". NPR. Retrieved 2022-01-15.
- ^ Lebot, Vincent (2020). Tropical Root and Tuber Crops : Cassava, Sweet Potato, Yams And Aroids. Wallingford, Oxfordshire, UK Boston, USA: CABI (Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International). p. 541. ISBN 978-1-78924-336-9. OCLC 1110672215.
- ^ Soucy, Shannon M.; Huang, Jinling; Gogarten, Johann Peter (2015-07-17). "Horizontal gene transfer: building the web of life". Nature Reviews Genetics. 16 (8). Nature Portfolio: 472–482. doi:10.1038/nrg3962. ISSN 1471-0056. PMID 26184597. S2CID 6794788.
- ^ Andersen, Martin Marchman; Landes, Xavier; Xiang, Wen; Anyshchenko, Artem; Falhof, Janus; Østerberg, Jeppe Thulin; Olsen, Lene Irene; Edenbrandt, Anna Kristina; Vedel, Suzanne Elizabeth; Thorsen, Bo Jellesmark; Sandøe, Peter; Gamborg, Christian; Kappel, Klemens; Palmgren, Michael G. (2015). "Feasibility of new breeding techniques for organic farming". Trends in Plant Science. 20 (7). Cell Press: 426–434. Bibcode:2015TPS....20..426A. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2015.04.011. ISSN 1360-1385. PMID 26027462. S2CID 205454618.
- ^ a b Gonsalves, D. (2004). "Transgenic papaya in Hawaii and beyond". AgBioForum. 7 (1&2): 36–40. Archived from the original on 2010-07-06. Retrieved 2013-01-20.
- ^ "The Rainbow Papaya Story". Hawaii Papaya Industry Association. Archived from the original on 2015-01-07. Retrieved April 17, 2015.
- ^ a b Ronald, Pamela; McWilliams, James (May 14, 2010). "Genetically Engineered Distortions". The New York Times. Retrieved July 26, 2010.
- ^ Li, Y; et al. (April 2014). "Biosafety management and commercial use of genetically modified crops in China". Plant Cell Reports. 33 (4): 565–73. doi:10.1007/s00299-014-1567-x. PMID 24493253. S2CID 16570688.
- ^ Loo, Jacky Fong-Chuen; But, Grace Wing-Chiu; Kwok, Ho-Chin; Lau, Pui-Man; Kong, Siu-Kai; Ho, Ho-Pui; Shaw, Pang-Chui (2019). "A rapid sample-to-answer analytical detection of genetically modified papaya using loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay on lab-on-a-disc for field use". Food Chemistry. 274: 822–830. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.049. ISSN 0308-8146. PMID 30373016. S2CID 53115420.
- ^ "Genetically Modified Organisms (Control of Release) Ordinance Cap. 607: Review of the Exemption of Genetically Modified Papayas in Hong Kong" (PDF).
- ^ Bawa, A. S.; Anilakumar, K. R. (2016-12-04). "Genetically modified foods: safety, risks and public concerns – a review". Journal of Food Science and Technology. 50 (6): 1035–46. doi:10.1007/s13197-012-0899-1. ISSN 0022-1155. PMC 3791249. PMID 24426015.
- ^ "Business BASF applies for approval for another biotech potato". Research in Germany. November 17, 2011. Archived from the original on June 2, 2013. Retrieved October 18, 2012.
- ^ Burger, Ludwig (October 31, 2011). "BASF applies for EU approval for Fortuna GM potato". Reuters. Frankfurt. Retrieved December 29, 2011.
- ^ Turley, Andrew (February 7, 2013). "BASF drops GM potato projects". Royal Society of Chemistry News.
- ^ "The History and Future of GM Potatoes". Potatopro.com. 2010-03-10. Archived from the original on 2013-10-12. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ^ Pollack, Andrew (November 7, 2014). "U.S.D.A. Approves Modified Potato. Next Up: French Fry Fans". The New York Times.
- ^ "Availability of Petition for Determination of Nonregulated Status of Potato Genetically Engineered for Low Acrylamide Potential and Reduced Black Spot Bruise". Federal Register. May 3, 2013.
- ^ Johnson, Stanley R. (February 2008). "Quantification of the Impacts on US Agriculture of Biotechnology-Derived Crops Planted in 2006" (PDF). Washington, D.C.: National Center for Food and Agricultural Policy. Retrieved August 12, 2010.
- ^ "GMO Database: Zucchini (courgette)". GMO Compass. November 7, 2007. Archived from the original on February 25, 2017. Retrieved February 28, 2015.
- ^ Perkowski, Mateusz (April 16, 2013). "Del Monte Gets Approval to Import GMO Pineapple". Food Democracy Now. Archived from the original on April 22, 2013.
- ^ Bradley, Diana (27 October 2020). "Inside the sweet and successful launch of the world's first pink pineapple". PRWeek. Retrieved 10 July 2021.
- ^ Pollack, A. (February 13, 2015). "Gene-Altered Apples Get U.S. Approval". The New York Times.
- ^ Tennille, Tracy (February 13, 2015). "First Genetically Modified Apple Approved for Sale in U.S." The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved February 13, 2015.
- ^ "How'd we 'make' a nonbrowning apple?". Okanagan Specialty Fruits. 2011-12-07. Archived from the original on 2019-08-12. Retrieved September 19, 2016.
- ^ "Know Before You Grow". National Corn Growers Association. Archived from the original on October 23, 2011.
- ^ "Acreage NASS" (PDF). National Agricultural Statistics Board annual report. June 2010. Retrieved July 23, 2010.
- ^ "Corn-Based Food Production in South Dakota: A Preliminary Feasibility Study" (PDF). South Dakota State University, College of Agriculture and Biological Sciences, Agricultural Experiment Station. June 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2013-01-19.
- ^ Padgette SR, et al (1995) Development, identification, and characterization of a glyphosate-tolerant soybean line. Crop Sci 35:1451-1461.
- ^ Ye X, Al-Babili S, Klöti A, Zhang J, Lucca P, Beyer P, Potrykus I (January 2000). "Engineering the provitamin A (beta-carotene) biosynthetic pathway into (carotenoid-free) rice endosperm". Science. 287 (5451): 303–5. Bibcode:2000Sci...287..303Y. doi:10.1126/science.287.5451.303. PMID 10634784. S2CID 40258379.
- ^ Frist B (21 November 2006). "'Green revolution' hero". Washington Times.
One existing crop, genetically engineered "golden rice" that produces vitamin A, already holds enormous promise for reducing blindness and dwarfism that result from a vitamin-A deficient diet.
- ^ Black RE, Allen LH, Bhutta ZA, Caulfield LE, de Onis M, Ezzati M, Mathers C, Rivera J (January 2008). "Maternal and child undernutrition: global and regional exposures and health consequences". Lancet. 371 (9608): 243–60. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61690-0. PMID 18207566. S2CID 3910132.
- ^ Humphrey JH, West KP, Sommer A (1992). "Vitamin A deficiency and attributable mortality among under-5-year-olds". Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 70 (2): 225–32. PMC 2393289. PMID 1600583.
- ^ Paine JA, Shipton CA, Chaggar S, Howells RM, Kennedy MJ, Vernon G, Wright SY, Hinchliffe E, Adams JL, Silverstone AL, Drake R (April 2005). "Improving the nutritional value of Golden Rice through increased pro-vitamin A content". Nature Biotechnology. 23 (4): 482–7. doi:10.1038/nbt1082. PMID 15793573. S2CID 632005.
- ^ "US FDA approves GMO Golden Rice as safe to eat". Genetic Literacy Project. 2018-05-29. Retrieved 2018-05-30.
- ^ Staff, USDA Economic Research Service. Last updated: January 24, 2013 Wheat Background
- ^ "Petitions for Determination of Nonregulated Status". USDA. Archived from the original on 29 April 2018. Retrieved 9 March 2018.
- ^ Regalado, Antonio. "These are not your father's GMOs". MIT Technology Review. Retrieved 9 March 2018.
- ^ Waltz, Emily (2016). "Gene-edited CRISPR mushroom escapes US regulation". Nature. 532 (7599). Nature Portfolio: 293. Bibcode:2016Natur.532..293W. doi:10.1038/nature.2016.19754. PMID 27111611.
- ^ Harper, G.S.; Brownlee, A.; Hall, T.E.; Seymour, R.; Lyons, R.; Ledwith, P. (2003). "Global progress toward transgenic food animals: A survey of publicly available information" (PDF). Food Standards Australia and New Zealand. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 13, 2020. Retrieved August 27, 2015.
- ^ Rick MacInnes-Rae, Rick (November 27, 2013). "GMO salmon firm clears one hurdle but still waits for key OKs AquaBounty began seeking American approval in 1995". CBC News.
- ^ Pollack, Andrew (May 21, 2012). "An Entrepreneur Bankrolls a Genetically Engineered Salmon". The New York Times. Retrieved September 3, 2012.
- ^ Naik, Gautam (September 21, 2010). "Gene-Altered Fish Closer to Approval". The Wall Street Journal.
- ^ "FDA takes several actions involving genetically engineered plants and animals for food" (Press release). Office of the Commissioner of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 2015-12-03.
- ^ Coffey, Aidan; Ross, R. Paul (2002). "Bacteriophage-resistance systems in dairy starter strains: molecular analysis to application". Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 82 (1/4). Springer: 303–321. doi:10.1023/a:1020639717181. ISSN 0003-6072. PMID 12369198. S2CID 7217985.
- ^ O'Sullivan, Lisa; Bolton, Declan; McAuliffe, Olivia; Coffey, Aidan (2019-03-25). "Bacteriophages in Food Applications: From Foe to Friend". Annual Review of Food Science and Technology. 10 (1). Annual Reviews: 151–172. doi:10.1146/annurev-food-032818-121747. ISSN 1941-1413. PMID 30633564. S2CID 58620015.
- ^ a b "Lecithin". October 2015. Archived from the original on 1 November 2015. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ^ a b "Select Committee on GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Opinion: Lecithin". Food and Drug Administration. August 10, 2015. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ^ "Corn Oil, 5th Edition" (PDF). Corn Refiners Association. 2006.
- ^ a b c Jaffe, Greg (Director of Biotechnology at the Center for Science in the Public Interest) (February 7, 2013). "What You Need to Know About Genetically Engineered Food". Atlantic.
- ^ "Regulation (EC) 50/2000". Eur-lex.europa.eu.
- ^ Marx, Gertruida M. (December 2010). Monitoring of Genetically Modified Food Products in South Africa (PDF) (PhD dissertation). South Africa: University of the Free State. hdl:11660/1485. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-01-09.
- ^ Davison, John; Bertheau, Yves Bertheau (2007). "EU regulations on the traceability and detection of GMOs: difficulties in interpretation, implementation and compliance". CAB Reviews: Perspectives in Agriculture, Veterinary Science, Nutrition and Natural Resources. 2 (77). doi:10.1079/pavsnnr20072077.
- ^ "ISAAA Brief 43-2011. Executive Summary: Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2011". Isaaa.org. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ^ "Sugar beet". Archived from the original on 2016-03-01. Retrieved 2016-02-19.
- ^ Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2009). Sugar Beet: White Sugar (PDF). p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-05. Retrieved 2012-09-17.
- ^ Klein, Joachim; Altenbuchner, Josef; Mattes, Ralf (1998-02-26). "Nucleic acid and protein elimination during the sugar manufacturing process of conventional and transgenic sugar beets". Journal of Biotechnology. 60 (3): 145–53. doi:10.1016/S0168-1656(98)00006-6. PMID 9608751.
- ^ "Soyatech.com". Soyatech.com. Archived from the original on 2012-10-25. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ^ "Poster of corn products" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-02-14. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ^ "Food Fats and Oils" (PDF). Institute of Shortening and Edible Oils. 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-02-14. Retrieved 2011-11-19.
- ^ "Twenty Facts about Cottonseed Oil". National Cottonseed Producers Association. Archived from the original on October 17, 2015.
- ^ Simon, Michelle (August 24, 2011). "ConAgra Sued Over GMO '100% Natural' Cooking Oils". Food Safety News.
- ^ "ingredients of margarine". Imace.org. Archived from the original on February 25, 2012. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ^ "USDA Protein(g) in Fats and Oils". Archived from the original on 2018-10-05. Retrieved 2015-05-31.
- ^ Crevel, R.W.R.; Kerkhoff, M.A.T.; Koning, M.M.G (2000). "Allergenicity of refined vegetable oils". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 38 (4): 385–93. doi:10.1016/S0278-6915(99)00158-1. PMID 10722892.
- ^ "What is Canola Oil?". CanolaInfo. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ^ David Bennett for Southeast Farm Press, February 5, 2003 World soybean consumption quickens Archived 2006-06-05 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Soybean". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved February 18, 2012.
- ^ "2012 World of Corn, National Corn Growers Association" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-02-07. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ^ Staff, GMO Compass. December 7, 2006. Genetic Engineering: Feeding the EU's Livestock Archived 2017-01-12 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Snell, C; Bernheim, A; Berge, JB; Kuntz, M; Pascal, G; Paris, A; Ricroch, AE (2012). "Assessment of the health impact of GM plant diets in long-term and multigenerational animal feeding trials: A literature review". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 50 (3–4): 1134–48. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2011.11.048. PMID 22155268.
- ^ Fellows, P.J. (2009). Food Processing Technology: Principles and Practice. Woodhead Publishing Limited. p. 236. ISBN 978-1845692162.
- ^ Gerdes, Louise. Genetic Engineering Opposing Viewpoints (2004 ed.). Greenhaven Press. p. 132.
- ^ Taylor, Steve; Hefle, Susan (May 2001). "Will genetically modified foods be allergenic?". Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 107 (5): 765–771. doi:10.1067/mai.2001.114241. PMID 11344340.
- ^ Emtage, JS; Angal, S; Doel, MT; Harris, TJ; Jenkins, B; Lilley, G; Lowe, PA (1983). "Synthesis of calf prochymosin (prorennin) in Escherichia coli". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 80 (12): 3671–75. Bibcode:1983PNAS...80.3671E. doi:10.1073/pnas.80.12.3671. PMC 394112. PMID 6304731.
- ^ Harris TJ, Lowe PA, Lyons A, Thomas PG, Eaton MA, Millican TA, Patel TP, Bose CC, Carey NH, Doel MT (April 1982). "Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA coding for calf preprochymosin". Nucleic Acids Research. 10 (7): 2177–87. doi:10.1093/nar/10.7.2177. PMC 320601. PMID 6283469.
- ^ a b c "Chymosin". GMO Compass. Archived from the original on 2015-03-26. Retrieved 2016-11-03.
- ^ Law, Barry A. (2010). Technology of Cheesemaking. UK: Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 100–101. ISBN 978-1-4051-8298-0.
- ^ "Food Biotechnology in the United States: Science, Regulation, and Issues". U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 2006-08-14.
- ^ Johnson, M.E.; Lucey, J.A. (2006). "Major Technological Advances and Trends in Cheese". Journal of Dairy Science. 89 (4): 1174–78. doi:10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(06)72186-5. PMID 16537950.
- ^ Baumana, Dale E.; Collier, Robert J. (September 15, 2010). "Use of Bovine Somatotropin in Dairy Production" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on May 13, 2013. Retrieved February 23, 2013.
- ^ Staff (2011-02-18). Last Medical Review. American Cancer Society.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help); Missing or empty|url=(help)[full citation needed] - ^ "Recombinant Bovine Growth Hormone". www.cancer.org.
- ^ Brennand, Charlotte P. "Bovine Somatotropin in Milk" (PDF). Retrieved 2011-03-06.
- ^ Cima, Greg (November 18, 2010). "Appellate court gives mixed ruling on Ohio rBST labeling rules". JAVMA News.
- ^ a b leafcom. "International Dairy Foods Ass'n v. Boggs – Argued: June 10, 2010". Leagle.com.
- ^ a b c d e Costa-Font, Montserrat; Gil, José M.; Traill, W. Bruce (April 2008). "Consumer acceptance, valuation of and attitudes towards genetically modified food: Review and implications for food policy". Food Policy. 33 (2): 99–111. doi:10.1016/j.foodpol.2007.07.002. ISSN 0306-9192.
- ^ "Genetically modified foods" (PDF). Public Health Association of Australia. 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 20, 2014.
- ^ a b c "CAPE's Position Statement on GMOs". Canadian Association of Physicians for the Environment. November 11, 2013. Archived from the original on March 26, 2014. Retrieved March 26, 2014.
- ^ a b "IDEA Position on Genetically Modified Foods". Irish Doctors' Environmental Association. Archived from the original on 2014-03-26. Retrieved 2014-03-25.
- ^ "American Academy of Environmental Medicine Calls for Immediate Moratorium on Genetically Modified Foods, position paper". American Academy of Environmental Medicine. Archived from the original on 1 March 2019. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- ^ "Press Advisory". American Academy of Environmental Medicine. Archived from the original on 28 April 2015. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ^ "Heterogeneity in consumer preferences for organic and genetically modified food products in Ghana" (PDF). African Journal of Agricultural and Resource Economics. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2022-11-28. Retrieved 2021-10-28.
- ^ "Can GMOs Be Used in Organic Products? | Agricultural Marketing Service". www.ams.usda.gov. Retrieved 28 October 2021.
- ^ Ashaolu, Tolulope J.; Ashaolu, Joseph O. (1 December 2020). "Perspectives on the trends, challenges and benefits of green, smart and organic (GSO) foods". International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science. 22: 100273. doi:10.1016/j.ijgfs.2020.100273. ISSN 1878-450X. PMC 7574864. PMID 33101552.
- ^ Emily Marden, Risk and Regulation: U.S. Regulatory Policy on Genetically Modified Food and Agriculture 44 B.C.L. Rev. 733 (2003).
- ^ "The History and Future of GM Potatoes". PotatoPro.com. 2013-12-11. Archived from the original on 2013-10-12. Retrieved 2012-09-17.
- ^ APPDMZ\ccvivr. "Commonly Asked Questions about the Food Safety of GMOs". monsanto.com.
- ^ Pollack, Andrew (2015-07-02). "White House Orders Review of Rules for Genetically Modified Crops". The New York Times. Retrieved 2015-07-03.
- ^ "Food from Genetically Engineered Plants". FDA. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ^ "Statement of Policy – Foods Derived from New Plant Varieties". Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ^ Andrew Pollack for The New York Times. September 23, 2000 "Kraft Recalls Taco Shells With Bioengineered Corn"
- ^ Genetically modified foods. Food Standards Agency. Retrieved 27 May 2024.
- ^ Genetic Technology Act key tool for UK food security. GOV.UK. 23 March 2023. Retrieved 27 May 2024.
- ^ Chokshi, Niraj (9 May 2014). "Vermont just passed the nation's first GMO food labeling law. Now it prepares to get sued". The Washington Post. Retrieved 19 January 2016.
- ^ "The Regulation of Genetically Modified Food". Archived from the original on 2017-06-10. Retrieved 2013-11-22.
- ^ Van Eenennaam, Alison; Chassy, Bruce; Kalaitzandonakes, Nicholas; Redick, Thomas (2014). "The Potential Impacts of Mandatory Labeling for Genetically Engineered Food in the United States" (PDF). Council for Agricultural Science and Technology (CAST). 54 (April 2014). ISSN 1070-0021. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-05-29. Retrieved 2014-05-28.
To date, no material differences in composition or safety of commercialized GE crops have been identified that would justify a label based on the GE nature of the product.
- ^ Hallenbeck, Terri (2014-04-27). "How GMO labeling came to pass in Vermont". Burlington Free Press. Retrieved 2014-05-28.
- ^ Botha, Gerda M.; Viljoen, Christopher D. (2009). "South Africa: A case study for voluntary GM labelling". Food Chemistry. 112 (4): 1060–64. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.06.050.
- ^ Davison, John (2010). "GM plants: Science, politics and EC regulations". Plant Science. 178 (2): 94–98. Bibcode:2010PlnSc.178...94D. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2009.12.005.
- ^ a b Wunderlich, Shahla; Kelsey A. Gatto (November 2015). "Consumer Perception of Genetically Modified Organisms and Sources of Information". Advances in Nutrition. 6 (6): 842–851. doi:10.3945/an.115.008870. PMC 4642419. PMID 26567205.
- ^ "EU GMO testing homepage". European Commission Join Research Centre. 2012-11-20. Retrieved May 31, 2015.
- ^ Costa, Joana; Mafra, Isabel; Amaral, Joana S.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. (2010). "Monitoring genetically modified soybean along the industrial soybean oil extraction and refining processes by polymerase chain reaction techniques". Food Research International. 43: 301–06. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2009.10.003.
- ^ "Redirecting..." heinonline.org. Archived from the original on 2019-01-23. Retrieved 2019-01-23.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ Gould F, Amasino RM, Brossard D, Buell CR, Dixon RA, Falck-Zepeda JB, et al. (September 2022). "Toward product-based regulation of crops". Science. 377 (6610): 1051–1053. Bibcode:2022Sci...377.1051G. doi:10.1126/science.abo3034. PMID 36048940. S2CID 252008948.
- Expert debate about the proposal: "Vorschlag zur Regulation von Zuchtpflanzen" (in German). Science Media Centre Germany. Retrieved 21 October 2022.
- University press release: "Researchers propose new framework for regulating engineered crops". North Carolina State University via phys.org. Retrieved 21 October 2022.
- News report: "Gentechnik soll kein Grund mehr für Verbote von Nutzpflanzen sein". DER STANDARD (in Austrian German). Retrieved 21 October 2022.
- ^ American Medical Association (2012). Report 2 of the Council on Science and Public Health: Labeling of Bioengineered Foods. Archived 2012-09-07 at the Wayback Machine "To better detect potential harms of bioengineered foods, the Council believes that pre-market safety assessment should shift from a voluntary notification process to a mandatory requirement." p. 7
- ^ Chartered Institute of Environmental Health (2006) Proposals for managing the coexistence of GM, conventional and organic crops Response to the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs consultation paper. Archived 2017-05-25 at the Wayback Machine October 2006
- ^ Paull, John (2013) "The threat of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) to organic agriculture: A case study update". Agriculture & Food, 3:.56-63
- ^ "About". Peel Back The Label. Retrieved 2021-07-09.
- ^ Knutson, Jonathan (May 22, 2018). "Dairy farmers fight back against deceptive advertising". Agweek. Retrieved 2021-07-09.
- ^ a b c d e f g Paparini, Andrea; Romano-Spica, Vincenzo (2004), Public health issues related with the consumption of food obtained from genetically modified organisms, Biotechnology Annual Review, vol. 10, Elsevier, pp. 85–122, doi:10.1016/s1387-2656(04)10004-5, ISBN 9780444517494, PMID 15504704, retrieved 2022-05-24
- ^ Prescott, Vanessa E.; Hogan, Simon P. (August 2006). "Genetically modified plants and food hypersensitivity diseases: Usage and implications of experimental models for risk assessment". Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 111 (2): 374–383. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.10.005. ISSN 0163-7258. PMID 16364445.
- ^ Ahmed, Farid E. (November 2003). "Genetically modified probiotics in foods". Trends in Biotechnology. 21 (11): 491–497. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2003.09.006. ISSN 0167-7799. PMID 14573362.
- ^ D'Agnolo, G. (August 2005). "GMO: Human Health Risk Assessment". Veterinary Research Communications. 29 (S2): 7–11. doi:10.1007/s11259-005-0003-7. ISSN 0165-7380. PMID 16244917. S2CID 12709929.
- ^ a b Watson, Ronald R. (2016). Genetically modified organisms in food production, safety, regulation and public health. Elsevier Science. ISBN 978-0-12-802530-7. OCLC 1281814112.
- ^ a b c Walters, Reece (2010-10-04). Eco Crime and Genetically Modified Food. Routledge-Cavendish. doi:10.4324/9780203844151. ISBN 978-1-136-91813-1.
- ^ a b c Hwang, Hyesun; Nam, Su-Jung (2020-11-02). "The influence of consumers' knowledge on their responses to genetically modified foods". GM Crops & Food. 12 (1): 146–157. doi:10.1080/21645698.2020.1840911. ISSN 2164-5698. PMC 7644159. PMID 33138666.
- ^ Lucht, Jan (2015-07-30). "Public Acceptance of Plant Biotechnology and GM Crops". Viruses. 7 (8): 4254–4281. doi:10.3390/v7082819. ISSN 1999-4915. PMC 4576180. PMID 26264020.
External links
[edit]- Library resources in your library and in other libraries about Genetically modified food
 Media related to Genetically modified food at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Genetically modified food at Wikimedia Commons